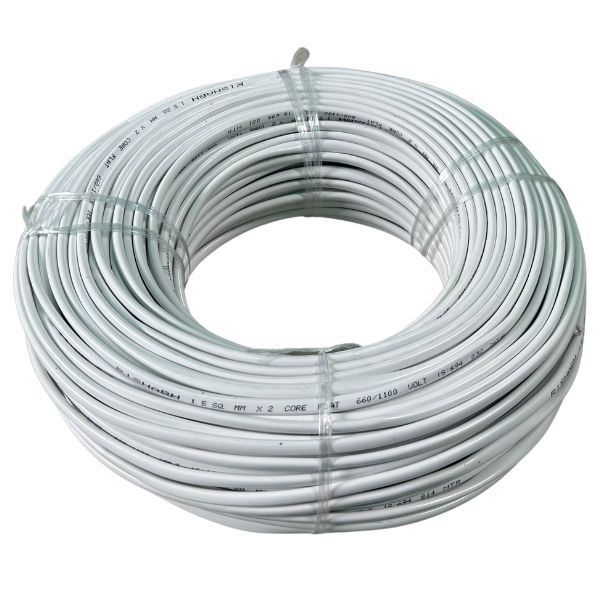
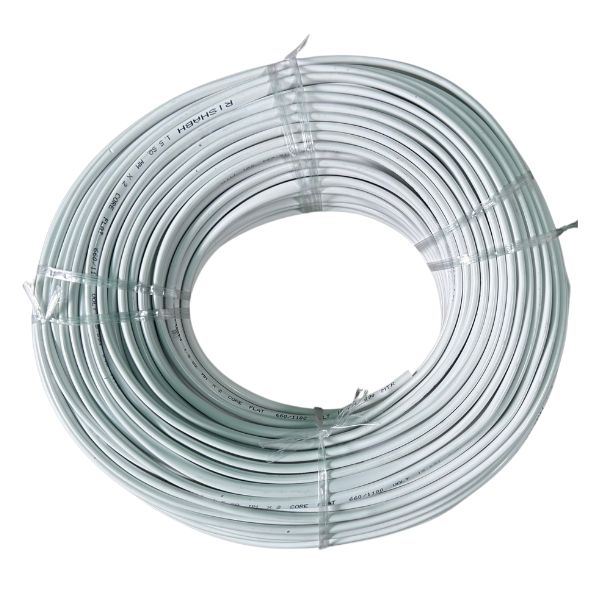
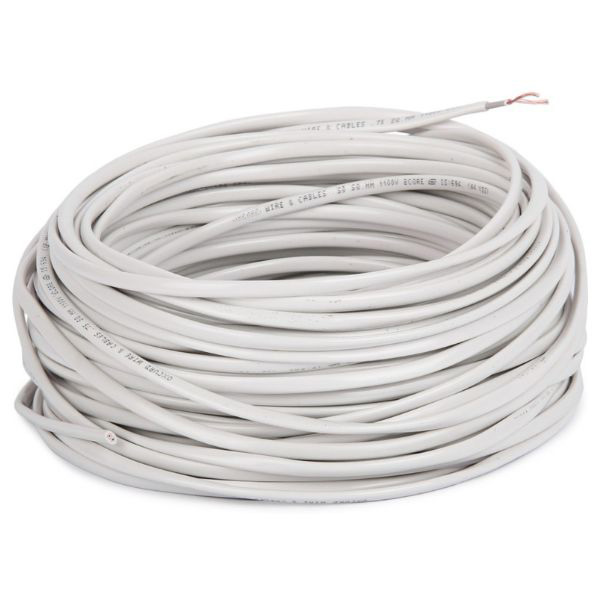
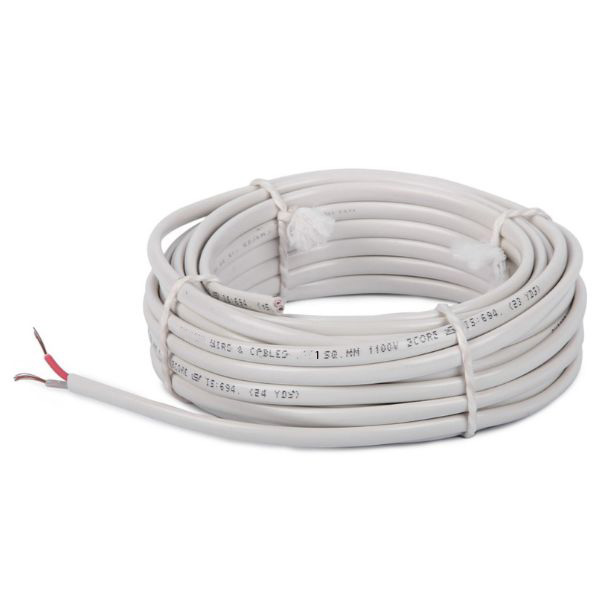
Rishabh 1.5 MM 2 Core Round Copper Wire Cable (30 Meter)
Rated 4.00 out of 5
(1)
Rishabh 1.5 MM 2 Core Round Copper Wire Cable (60 Meter)
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(1)
Rishabh 1.5 MM 2 Core Round Copper Wire Cable (90 Meter)
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(3)
1.0MM 2 Core Copper Flat Wire
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(1)
₹199.00 – ₹1,500.00
Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
0.75MM 2 Core Copper Flat Wire
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(1)
₹149.00 – ₹1,400.00
Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Polyflex 2.5MM 15 Meter 2 Core Copper Wire
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(3)
Bengal 4.0MM 2 Core Aluminium Cable (90 Meter)
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(2)
Bengal 2.5MM 2 Core Aluminium Cable (90 Meter)
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(2)
1.5MM Flat Copper 2 Core Wire (90 Meter)
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(8)
Bengal 10MM 2 Core Aluminium Cable (10 Meter)
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(1)
Polyflex 2.5mm 2 Core Flat Wire (90 Meter)
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(5)
- Flexibility: Polyflex 2.5mm 2 Core Flat Wire offers exceptional flexibility, making it easy to install in various settings without the risk of breakage or damage. This feature addresses the pain point of dealing with rigid wires that are difficult to maneuver, saving time and effort during installation.
- Durable Construction: Constructed with high-quality materials, this wire is built to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations and exposure to moisture or chemicals. Customers can rely on its durability for long-term use, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
- Space-saving Design: The flat design of the wire allows for efficient utilization of space, especially in tight or confined areas where traditional round wires may not fit properly. This feature is particularly advantageous in applications where space is limited, such as in automotive wiring or home appliances.
- High Conductivity: With excellent conductivity properties, the Polyflex wire ensures reliable electrical performance, minimizing the risk of signal loss or voltage drops. This benefit is crucial in applications where consistent power delivery is essential, such as in audio systems or industrial machinery.
- Easy Identification: The wire is color-coded for easy identification of polarity, simplifying the installation process and reducing the likelihood of wiring errors. This feature enhances efficiency and accuracy, saving time and minimizing the need for troubleshooting.
- Versatile Applications: Suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive, marine, industrial, and residential projects, the Polyflex wire offers versatility to customers across various industries. This versatility adds value by providing a single solution for multiple wiring needs, streamlining inventory management, and reducing costs.
23 by 76 Copper Flexible PVC Wire (90 Meter)
Rated 4.50 out of 5
(2)
40 by 76 Copper Flexible PVC Wire (15 Meter)
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(1)
Polyflex 1.5MM Flat Round 15M Copper 2 Core Wire
Rated 3.00 out of 5
(2)
Polyflex 1.5MM Flat Copper 2 Core Wire (30 Meter)
Rated 5.00 out of 5
(2)
Polyflex 2.5MM Round Copper 2 Core Wire (30 Meter)
Rated 4.90 out of 5
(10)
Polycab Optima 4.0MM Single Core 90M Wire
Rated 0 out of 5
Polycab Optima 1.0MM Single Core 90M Wire
Rated 0 out of 5
Load more products
Loading...
Copper wire is a versatile and widely used material in a variety of applications, ranging from electrical wiring and telecommunications to arts and crafts. Its popularity is largely due to its excellent electrical conductivity, ease of use, and durability. Here, we delve into a comprehensive overview of copper wire, covering its properties, types, manufacturing processes, applications, and considerations for its use.
Properties of Copper Wire
Copper wire is renowned for its superb electrical conductivity. It is second only to silver among the materials used for electrical applications but is much more cost-effective, making it the material of choice in electrical circuits. Copper is highly ductile, meaning it can be stretched into a thin wire without breaking. This ductility allows manufacturers to produce wire in various diameters and strengths, suitable for different uses.
Thermal conductivity is another significant property of copper wire, which enables it to carry heat away from components like electrical motors and transformers, reducing the risk of overheating and improving performance. The metal also exhibits good corrosion resistance, especially against environments that would typically corrode other metals. Copper naturally forms a protective layer of dark brown-black copper oxide which can protect the deeper layers from further corrosion.
Types of Copper Wire
There are several types of copper wire, each suited to specific applications:
- Solid Copper Wire: This type consists of a single, solid strand of copper. It's used where rigidity is necessary, such as in permanent installations within buildings or as antenna wire.
- Stranded Copper Wire: Comprising multiple strands of copper wire twisted together, this type is more flexible than solid wire. It is ideal for applications where the wire needs to bend or twist without breaking, such as in automotive wiring or in movable machine parts.
- Bare Copper Wire: Without any insulation, this type is used in overhead power sources where it does not need protection from environmental factors.
- Insulated Copper Wire: This type includes one or more conductive copper wires wrapped in a protective, non-conductive cover. Insulation prevents the wires from coming into contact with other conductive materials, reduces the leakage of current, and protects against environmental hazards like moisture.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of copper wire involves several key steps. It begins with the mining of copper ore, which is then ground into a fine powder, mixed with water, and subjected to froth flotation to separate the copper from other minerals. The copper is then smelted to remove impurities and refined to achieve the desired purity level.
The purified copper is cast into large rectangular billets that are heated and extruded through a die to create long, thin lengths of solid wire. For stranded wire, multiple thin wires are twisted together. Finally, the wire may be annealed, a process that involves heating and then slowly cooling the wire to remove stresses and improve flexibility.
Applications of Copper Wire
The applications of copper wire are vast and varied:
- Electrical Wiring: Used extensively in building construction for power and telecommunications wiring.
- Electronics: Essential in the creation of coils, transformers, and other electronic components.
- Telecommunications: Key component in the infrastructure for telephone and internet services, including the wiring and cables within networks.
- Automotive: Used in the electrical wiring systems of vehicles, including in batteries, lighting, and entertainment systems.
- Arts and Crafts: Copper wire is also popular in jewelry making, sculpture, and other craft projects due to its flexibility and color.
Considerations for Use
When selecting copper wire for specific applications, several factors must be considered:
- Gauge: The thickness of the wire affects its current-carrying capacity and resistance. Thicker wires can carry more current and have lower resistance.
- Insulation Type: The choice of insulation depends on environmental factors such as temperature, chemical exposure, and physical wear.
- Flexibility Needs: Depending on the application, the choice between solid and stranded wire must be made.
- Corrosion Resistance: While copper is corrosion-resistant, different environments may require additional coatings or protections.
Copper wire’s excellent electrical and thermal conductivities, coupled with its adaptability and durability, make it an indispensable material in modern technology. Whether in the electrical grid, electronics, or creative arts, its roles are critical and its benefits, undeniable. The careful selection of the type and specifications of copper wire can lead to optimal performance and efficiency in any application.